How does DLNA work? What are the specific application scenarios?
The DLNA protocol is a screencast protocol that allows mobile phones, computers, and various electrical appliances to communicate with each other through wireless or wired networks, making content sharing possible.
DLNA is file based, media files may have a variety of encoding formats, the player side must be able to handle so many encoding formats.
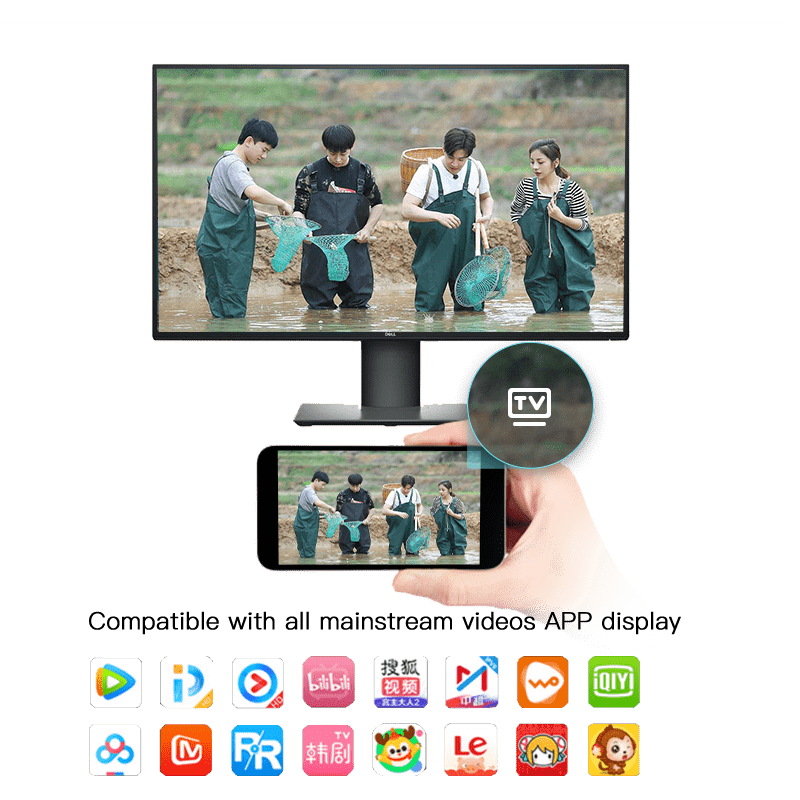
The most common application is that we can often see such a small TV icon with “TV” logo on mobile apps of various video platforms — push projection mode.
What are the specific application scenarios?
In fact, DLNA’s application is not just applied to the screen, in fact, it may be completely integrated into everyone’s life.
In terms of home devices, the most common are TV sets, NAS servers, webcams, TV boxes, smart speakers, printers and so on. In terms of mobile devices, common are mobile phones, tablets, laptops, portable players, cameras.
In addition to hardware support, it also needs software compatibility. Basically, the mainstream video APP now supports push wireless projection screen.
What is the principle?
After the phone searches for the TV, the phone sends a link to the address of a video resource to the TV. The TV connects to the link to get the video file and start playing it online. The phone can control the TV’s progress, volume and other commands.
Therefore, you will find that in order to use the projection function properly, whether it is smart TV or the same screen, you must connect the smart TV or the same screen to Wi-Fi, and the Wi-Fi must be able to access the Internet properly, then the projection function can be used normally.
The wireless projection function that comes with a typical mobile phone does not need to be concerned about whether the Wi-Fi can connect to the Internet.